Royal dorado, pink dorado or gray dorado: how to choose?"
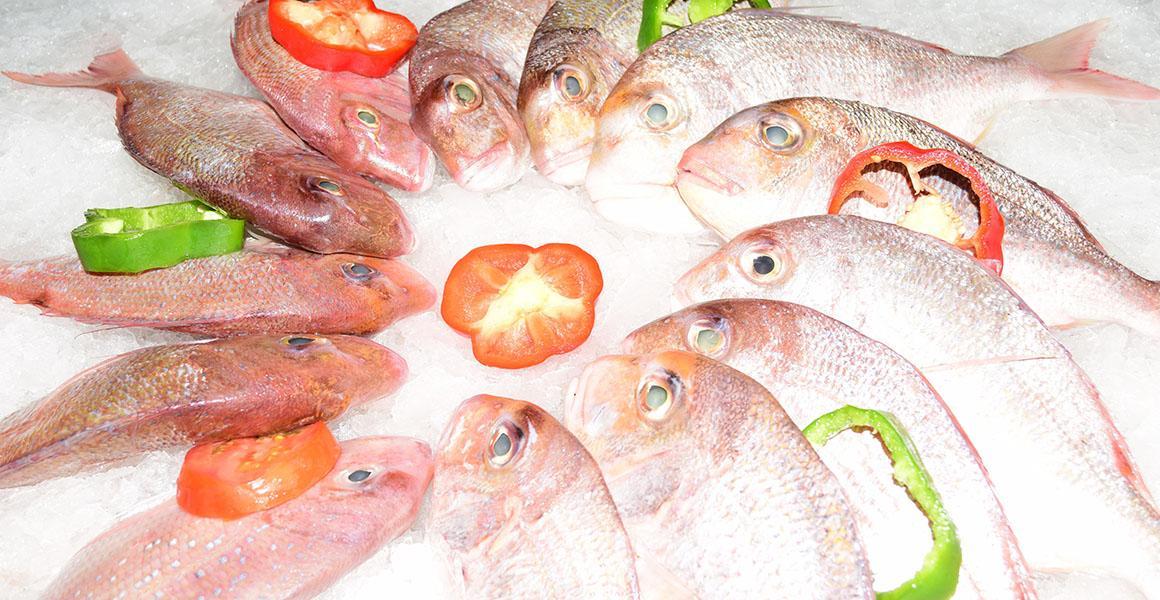

The term "daurade" (or "dorade") is used to refer to three species of fish: the royal dorado, the gray dorado, and the pink dorado, also known as pink pageot. How can you tell the difference between these species? What are their nutritional contributions? In which recipes are they found?
The royal dorado
The royal dorado is a fish in the Sparidae family. It measures 30 to 50 cm long and weighs up to 3 kg. The royal dorado, whose scientific name is Sparus aurata, is found in the Atlantic and Mediterranean. It is lean due to its low fat content.
The physical characteristics of the royal dorado
The royal dorado has particular characteristics that allow it to be differentiated from other species. You will recognize it with:
- The black spot it has on each ear;
- The golden crescent between its eyes, all on its massive head;
- Its silver-colored scales; Its very white, very fine and tender flesh;
- Its oval body;
- Its back of a blue-gray color;
- Its mouth has 4 to 6 canines accompanied by 2 to 4 rows of molars. The royal dorado is the most delicious species. It also has the particularity of being the subject of aquaculture, which makes it more accessible all year round.
Primarily carnivorous and occasionally herbivorous, the royal dorado feeds on mollusks, mussels, and crustaceans. It is marketed when it is at least 30 cm long. Very digestible, it can be consumed during a weight loss diet.
The nutritional qualities of the royal dorado
The royal dorado has an excellent reputation and is highly appreciated by gourmets. It is rich in omega-3 and proteins. It also provides omega-6 to the body.
The pink dorado
The pink pageot (Pagellus bogaraveo) also has a black spot on its ears. The pink dorado has the same dimensions as the royal dorado, but is considered less tasty. It is generally caught in the waters of the Atlantic, but its fishing is subject to very strict regulations. In fact, it is an endangered species, as it is widely exploited.
How to differentiate it from other species?
The pink dorado is characterized by the presence of:
- large eyes compared to its head;
- a small mouth; pink fins;
- a pink back at adulthood (beige color for juveniles).
The nutritional qualities of the pink dorado
The pink dorado, lean and digestible, is low in calories and provides little fat (1 g per 100 g of flesh). It is also appreciated for its mineral (phosphorus, calcium, iron) and trace element (iodine, zinc) contributions. It also contains proteins (16 g per 100 g of flesh) and vitamins B12, E.
The gray dorado
The gray dorado, whose scientific name is Lithognathus mormyrus, is found in the Atlantic, Mediterranean, and Black Sea. It is a predatory species that feeds on small fish, cephalopods, and crustaceans. It is characterized by a robust body, a large head, and a mouth with sharp teeth. It is less appreciated by consumers because of its coarser flesh. It is generally caught in the waters of the Atlantic, but its fishing is subject to very strict regulations. In fact, it is an endangered species, as it is widely exploited.
How to recognize the grey gurnard? This species is characterized by:
Its flat and long body; Its blue-gray color; Its grayish scales without reflections. The nutritional qualities of the grey gurnard The grey gurnard provides an interesting supply of nutrients. Like other species, it is a source of protein, omega-3, fats, vitamins B12 and carbohydrates (traces).
Despite its richness, this gurnard should be consumed in moderation, as 69 g of cholesterol are found in 100 g of its flesh. In addition, its great longevity exposes it to contamination and accumulation of mercury. Pregnant women and children should therefore consume it in moderation.
Some useful information Gurnards are hermaphroditic fish that change sex during their lives (like snails). Thus, the grey gurnard is born female and then becomes male over time. The opposite phenomenon is observed with pink and royal gurnards. This characteristic contributes to the problems of the balance of sexes and reproduction of these fish. This leads man to intervene through aquaculture activities.
The farmed gurnard (less delicious than wild gurnard) is available all year round, fresh or frozen. The period from February to September is when one finds much more wild gurnard in the sea.
Criteria for choosing a good gurnard To choose a quality gurnard, make sure its smell is pleasant and light. It must have a shiny, rigid and firm body. The gurnard must also have bulging, lively and shiny eyes with adherent scales.
How to cook the gurnard?
The gurnard can be cooked in a thousand ways. To do this, it must first be well prepared. Since it is usually bought whole, it must first be emptied and scaled. Then it can be cooked. The gurnard is often found in many traditional dishes such as zarzuéla, paëlla, and other fish soups.
Gurnard fillets can be steamed, boiled in court-bouillon or braised in white wine. They will then be cooked in a pan with olive oil (or white wine) and fresh herbs.
Whole gurnard can be baked or grilled on a barbecue, skewer, in parchment paper or fried. It is also delicious when cooked after being floured in butter in a pan. Similarly, it can be stuffed with a mixture of fine herbs, chopped vegetables, small shrimp or eaten in a tomato sauce.
In addition, gurnard with its delicate flesh can be consumed raw, in Japanese dishes such as sashimi or sushi.